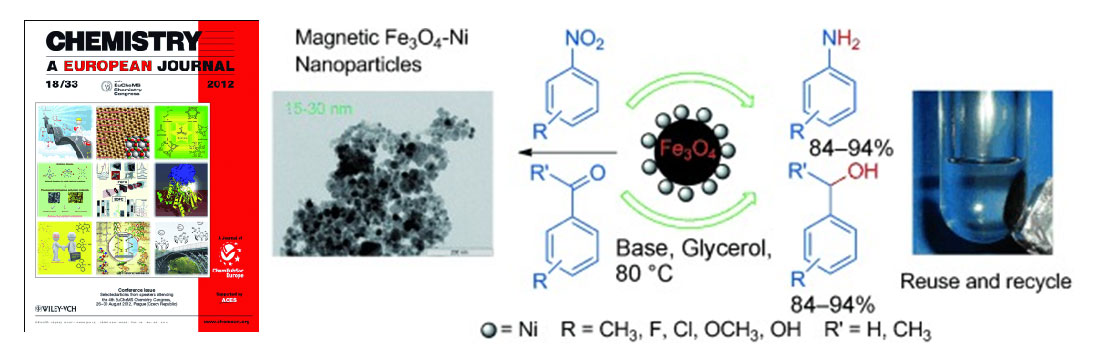
Gawande et al. article entitled “Regio- and Chemoselective reduction of nitroarenes and carbonyl compounds over recyclable magnetic Ferrite-Nickel nanoparticles (Fe3O4-Ni) by using glycerol as a hydrogen source” published in Chemistry – A European Journal, also Highlighted in Synfacts, 2012.
30.08.2012
Functionalized magnetic nanoparticles (MNPs) become known alternative for the conventional catalyst not only for homogeneous but also heterogeneous catalysis due to its magnetically separable nature which avoids catalyst filtration and easily recovered after the chemical transformation. Free nano-g-Fe2O3 is highly active, stable, and selective catalysts for various oxidations with high turnover number (TON) and excellent selectivity. Gawande et al. reported synthesis of Fe3O4-Ni MNPs by the simple wet impregnation method followed by chemical reduction by using inexpensive precursors, and without resource to linkers or ligands. Fe3O4 -Ni MNPs are highly efficient, viable heterogeneous catalysts employed for hydrogen-transfer reactions by using the environmentally friendly solvent glycerol as a hydrogen donor. In this article author successfully demonstrated a facile, simple and environmentally friendly hydrogen‐transfer reaction that occurs by catalytically recyclable ferrite–nickel magnetic nanoparticles (Fe3O4-Ni) by using glycerol as hydrogen source that employed for the synthesis of aromatic amines and alcohols from the precursor nitroarenes and carbonyl compounds.
Chemistry-A European Journal 2012, 18, 12628. (IF- 5.83);
Web: https://chemistry-europe.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/chem.201202380
Highlighted in Synfacts, 2012 8 (12) 1388, y013212sf
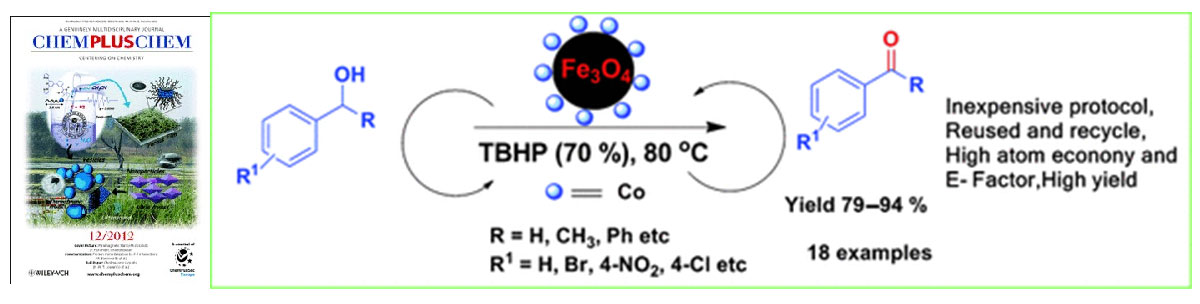
Gawande et al. article entitled “A Recyclable Ferrite–Co Magnetic Nanocatalyst for the Oxidation of Alcohols to Carbonyl Compounds” published in ChemPlusChem and “Cited as HOT TOPICS Magnetic Materials”, 2012.
10.08.2012
Oxidation of alcohols into carbonyl compounds is one of the most important and fascinating reactions in organic chemistry which utilized as valuable raw material for the chemical and pharmaceutical industries. Nowadays, various catalysts used for oxidation reaction in which functionalized magnetic nanoparticles (MNPs) are heterogeneous catalyst supports are viable alternatives to conventional materials because they are robust, inert, inexpensive, reusable, and recyclable using a simple magnet. Herein Gawande et al. reported synthesis of Ferrite–Co magnetic nanoparticles (Fe3O4–Co MNPs) by the simple wet impregnation method followed by chemical reduction. Due to higher catalytic efficiency Fe3O4–Co MNPs employed for the oxidation of alcohols into carbonyl compounds using tert‐butyl hydroperoxide (TBHP) as the oxidant. This robust magnetically separable and inexpensive nanocatalyst is highly cost-effective and environment friendly.
ChemPlusChem, 2012, 77, 865-871. (IF- 3.01) “Cited as HOT TOPICS Magnetic Materials”
Web: https://chemistry-europe.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/cplu.201200081
Cited as HOT TOPICS Magnetic Materials: (http://www.wiley-vch.de/util/hottopics/magnetic/)
Gawande et al. article entitled “Mixed metal MgO-ZrO2 nanoparticle-catalyzed O-tert-boc protection of alcohols, phenols under solvent-free conditions” published in Applied Organometallic Chemistry, also selected as, “Hottest article in Catalysis”, 2012.
27.06.2012
multistep drug synthesis, functional group protection having great attention due to synthetically important target molecule synthesis as well as to avoid side reaction and get selectivity during the chemical conversion. Protection and deprotection of alcohols and phenols having fundamental importance in multistep drug synthesis because of simplicity and mildness in preparing and removing the specific function. Gawande et al. reported an environmentally benign method for O-tert-Boc protection of alcohols and phenols catalyzed by MgO–ZrO2 nanoparticles (NPs) under solvent-free conditions. The MgO–ZrO2 NPs prepared by simple ultra-dilution procedure by using inexpensive precursors and are reusable, recyclable and chemoselective.
Applied Organometallic Chemistry, 2012, 26, 395-400. (IF- 3.5),
Web: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/aoc.2846
Web- “Hottest article in Catalysis”:
http://wileyasia.wordpress.com/2012/10/17/hottest-articles-in-catalysis/
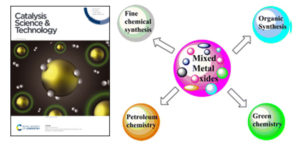
Gawande et al. article entitled “Role of mixed metal oxides in catalysis science - A versatile application in organic synthesis published in Catalysis Science and Technology, also in “Top ten articles 2012”.
03.02.2012
Metal oxides represent one of the most important classes of solid catalysts, either as active phases or as supports. Metal and mixed metal oxide used as a catalyst due to its fascinating properties like higher surface area as well as catalytic efficiency for organic transformations. Mixed metal oxides are oxygen-containing combinations of two or more metallic ions having wide scope in organic reactions, green chemistry also in industrial applications like ceramics, electronics, nuclear research as well as in catalysis. In the pharmaceutical industry, mixed metal oxides are widely utilized for organic conversions. In this mini-review significance of a variety of mixed metal oxides as catalysts and catalyst supports as employed for various catalytic applications both in the liquid and gaseous phases are discussed. Gawande et al. Summarized versatile applications of mixed metal oxides in organic synthesis such as reduction, oxidation, multicomponent, Mannich, alkylation, condensation, deprotection, cycloaddition, hydroxylation, dehydration, dehydrogenation, transesterification reactions involving biomimetic oxygen-evolving catalysts and other important C–C bond-forming reactions.
Catal. Sci. and Tech. 2012, 2, 1113-1125. (IF- 5.72) “Top ten article 2012”
Web-Top ten articles: http://blogs.rsc.org/cy/author/bandook/
Web: https://pubs.rsc.org/en/Content/ArticleLanding/2012/CY/C2CY00490A#!divAbstract