Dr. Gawande, Received the “Deans Award” from Dean of Palakcy Universtiy for the best publication output in the Chemistry Discipline.
07.12.2016

Gawande et al. review article “Cu and Cu-based nanoparticles: Synthesis and Applications in Catalysis” published in Chemical Reviews, 2016.
03.03.2016
Nanoparticles (NPs) having higher catalytic activity which represents a rich resource for chemical transformations, including both in industry and in academia. Cu is a 3d transition metal and has interesting physical As well as chemical properties. Cu-based materials utlilized for variety of reactions due to Cu’s wide range of accessible oxidation states. In this review, Gawande et al. summerised the uses of Cu and Cu-based NPs as catalysts for wide scope reactions, including reduction, oxidation, A3 coupling, electrocatalysis, photocatalysis, and gas-phase reactions. The synthetic strategies and relevant applications of Cu and Cu-based NPs are also discussed with brief descriptions along with characterization techniques. Most of the chemistries detailed in this review, namely, reactions in benign media, such as water, high turnover numbers (TON) and turnover frequencies (TOF), and magnetic recyclability with current devlopmemts in the field also included. This review article helpful for scientist to devlop novel methods on Cu and Cu based nanoparticles synthesis as well as exploring its application in the fields of nanotechnology, chemical engineering, organic chemistry, inorganic chemistry, and materials chemistry.
Key words : Copper Nanoparticles synthesis, Copper Nanopartcles Applications, Copper Catalysis, Copper Catalysts, Copper electrocatalysis, Copper Photocatalysis, Copper Synthesis
Chem. Rev. 2016, 116 (6), 3722–3811. (IF- 52.36), Highly Cited Article
Web: https://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/acs.chemrev.5b00482

Datta et al. article entitled “Base-free Transfer Hydrogenation of Nitroarenes Catalyzed by Micro-mesoporous Iron Oxide” published in ChemCatChem and “Selected for Front Cover”, 2016.
27.06.2016
Aniline and its derivatives are widely used as important organic intermediates in the chemical industry for the production of pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, polymers, and dyes. From different methods, the reduction of nitroarenes is one way to the synthesis of functionalized anilines. In this research article Datta et al. described micro-mesoporous iron oxide (MMIO) catalyst for the transfer hydrogenation of nitroarenes using biomass-derived formic acid as a reducing agent. The reduction of nitroarenes is achieved using flower-shaped micro-mesoporous iron oxide with formic acid as a reducing agent and tris[(2-diphenylphosphino)- ethyl]phosphine as the ligand in the absence of an additional base.
ChemCatChem, 2016, 8, 2351–2355. (IF- 4.49) “Selected for Front cover”
Web: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/cctc.201600296
Wiley Interview webpage: https://chemistry-europe.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1002/cctc.201600791


Datta et al. article entitled “Pd@Pt Core-Shell Nanoparticles with Branched Dandelion-like Morphology as Highly Efficient Catalysts for Olefin Reduction“ published in Chemistry A European Journal and highlighted as “hot article and inside front cover page”, 2016.
01.01.2016
Synthesis of well-defined metal nanoparticles (NPs) with controlled morphology is focused due to their interesting catalytic, electronic, photonic, and sensing properties. In this research article Datta et al. developed a synthesis method for highly branched micro– mesoporous, bimetallic Pd@Pt core-shell NPs with unique dandelion-like morphology by using ascorbic acid as a reducing agent. Also, it described good catalytic efficacy of branched porous Pd@Pt NPs for the reduction of olefins using hydrazine hydrate as a reducing agent at room temperature.
Chem. Eur. J., 2016, 22, 1577-1581. (IF- 5.1) “Selected for hot paper and inside front cover”
Web: http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/chem.201503441/epdf


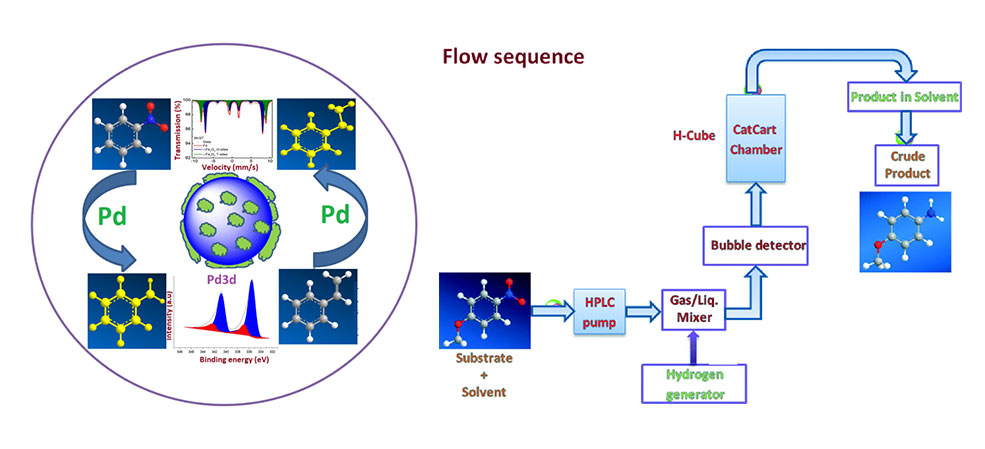
Our work on (Rathi et al.) “Continuous flow transfer hydrogenation of nitroarenes, azides and alkenes using maghemite-Pd nanocomposites" Published in Catalysis Science and Technology, 2016.
01.02.2016
We have reported continuous flow hydrogenation protocols for the reduction of nitroarenes, azides, and alkenes catalyzed by ultra-fine (1–3 nm) Pd nanoparticles supported on recyclable maghemite support. The product obtained with excellent yield under continuous flow and without any filtration. Pd nanoparticles supported maghemite catalyst is recyclable, lower metal loading, and there is no addition of additives required for flow reaction. The main aim of this research to develop an industrially favourable catalyst for the production of fine chemicals by implementing in large scale reactions.
Catalysis Science and Technology, 2016, 6, 152-160 (IF- 5.72)
Web: http://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlelanding/2016/cy/c5cy00956a#!divAbstract
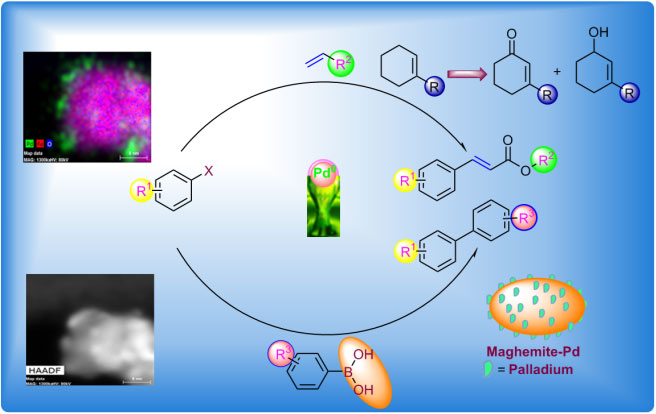
Rathi et al work entitled “Maghemite decorated with ultra-small palladium nanoparticles (γ-Fe2O3-Pd): applications in Heck-Mizoroki olefination, Suzuki reaction and allylic oxidation of alkenes“ published in Green Chemistry, 2016.
03.01.2016
In this reseach work, we have reported maghemite supported ultra-small Pd/PdO nanoparticles (~5 nm) useful for a variety of organic transformations namely Heck-Mizoroki olefination of aryl halides and Suzuki reaction with high yield in mild conditions and low catalyst loading. Also, the catalyst was effective for allylic oxidation of olefins. The developed system shows several superior features compared to other reported catalysts including very short reaction time for completion of the reaction (1-2 h), high yield and excellent selectivity, and reusability. The maghemite-Pd catalyst is recyclable and easily recovered by simple filtration or decantation.
Green Chem. 2016, 18, 2363-2373 (IF- 9.7) DOI: 10.1039/C5GC02264A.
Web: http://pubs.rsc.org/En/content/articlelanding/2015/gc/c5gc02264a#!divAbstract
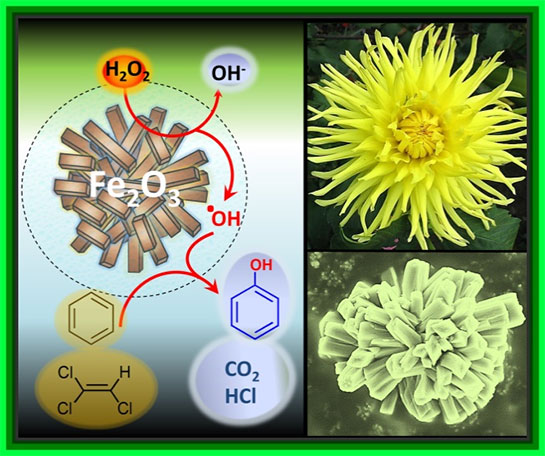
Datta et al. article entitled “Micro-Mesoporous Iron Oxides with Record Efficiency for Decomposition of Hydrogen Peroxide: Morphology Driven Catalysis for Degradation of Organic Contaminants “ published in Journal of Materials Chemistry A., 2016.
05.01.2016
Development of nanocatalyst for environmental remediation of organic/inorganic pollutants is crucial in environment benign catalysis. In this research work, Datta et al. reported a novel methodology for the synthesis of highly ordered micro-mesoporous nanocatalysts with an encoded 3D arrangement and extraordinary catalytic efficiency in the degradation of organic pollutants. Mesoporous and nanocrystalline iron-oxide-based heterogeneous catalysts represent an important class of earth-abundant materials. This precursor-based synthetic pathway allowed the successful assembly of a 3D rod/flower-like Fenton catalyst that exhibited the highest activity for the hydrogen peroxide decomposition.
J. Mater. Chem. A., 2016, 4, 596-604. (IF- 10.73)
Web: http://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlelanding/2015/ta/c5ta08386a#!divAbstract
Prof. Manoj B. Gawande, appointed as “Associate Editor” for Current Catalysis by Bentham Publications.
Heartly Congratulations !!! 2016

Bentham Science is a science, technology, and medical (STM) publisher, providing academic researchers and industrial professionals with the latest information in diverse fields of science and technology. Current Catalysis is an international peer-reviewed journal in Bentham Science, which publishes original research, full-length reviews/ mini reviews and thematic issues in all core areas of catalysis including theoretical, experimental and applied research. The aim of the journal is to publish the latest developments and to promote new ideas in the broad and multidisciplinary field of science. The topics covered heterogeneous catalysis, homogeneous catalysis, bio-catalysis, synthesis and properties of new catalysts including synthesis and catalytic function of novel inorganic solids and complexes.
Web: http://benthamscience.com/journals/current-catalysis/editorial-board/#top

