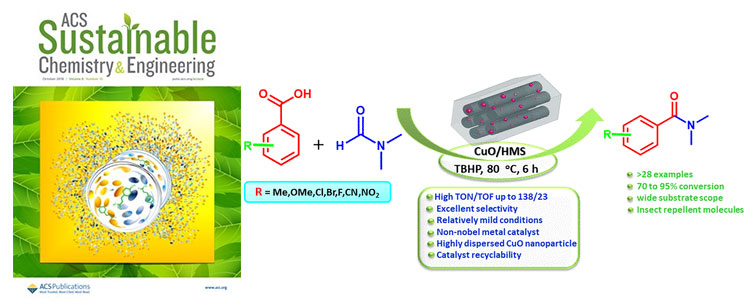
Kadam et al. article entitled “Hexagonal mesoporous silica supported ultrasmall copper oxides for oxidative amidation of carboxylic acids” published in ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2018.
22.08.2018
Kadam et al. reported the synthesis of hexagonal mesoporous silica (HMS) supported copper oxide nanoparticles by a one-pot sol-gel synthesis. The catalytic performance of HMS supported copper oxide nanoparticles is useful for oxidative amidation of carboxylic acids. The reaction protocol is environmentally benign due to its mild reaction conditions, high conversions and selectivity of catalyst. These catalyst also utilized for the variety of benzoic acid substituted functional groups conversion by reported reaction procedure. The scope of the reaction was extended for the synthesis of insect repellent bioactive molecules in grams scale.
ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2018, 6 (10), 12935–12945. (IF-6.97)
Web: https://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/acssuschemeng.8b02247
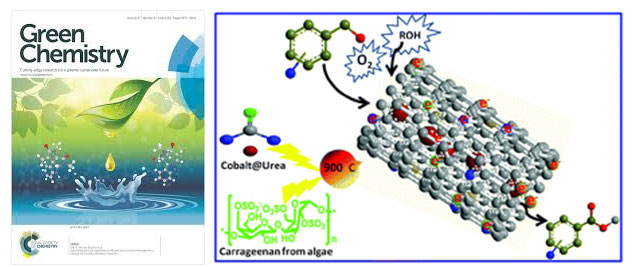
Nandan et al. article entitled “Cobalt-entrenched N-, O-, and S-tridoped carbons as efficient multifunctional sustainable catalysts for base-free selective oxidative esterification of alcohols” published in Green Chemistry, 2018.
21.06.2018
Now a days, nanomaterials has incredible attention due to their unique and versatile properties and numerous applications in various fields including energy conversion, chemical engineering, environmental and biological applications, and sustainable catalysis. In this research article, we have reported simple and environmentally friendly synthesis of sustainable and reusable non-noble transition-metal (cobalt) nanocatalysts containing N-, O-, and S-tridoped carbon nanotube (Co@NOSC) composites by using inexpensive and renewable carrageenan that provides carbon, oxygen, and sulfur entities and urea as a nitrogen source. The developed catalyst shows excellent catalytic performance towards base-free selective oxidative esterification of alcohols. This interesting protocol certainly opens the door to further material development by using renewable resources such as carrageenan that provides a rich source of sulfur and has specific gelling properties for specific target applications in catalysis, electrocatalysis, and photocatalysis.
Green Chem., 2018, 20, 3542-3556, (IF-9.4)
Web: https://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlelanding/2018/gc/c8gc01333k/unauth#!divAbstract
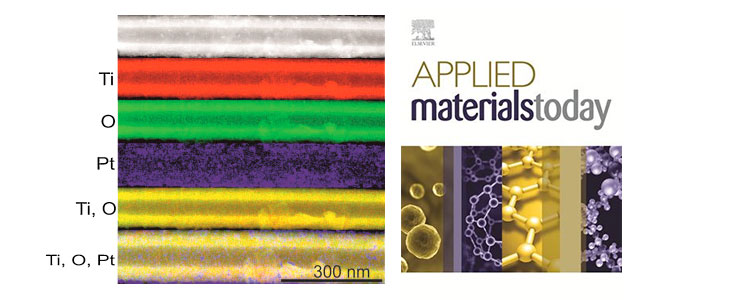
Anitha et al. work on “Pt nanoparticles decorated TiO2 nanotubes for the reduction of olefins” published in Applied Materials Today, 2018.
01.03.2018
Anitha et al. reported synthesis of high surface area TiO2 nanotubes (TNTs) used as a catalyst support for well dispersed, stable and ultra-small (3–5 nm) Pt nanoparticles (Pt@TNTs) for the reduction of olefins. Pt@TNT catalyst was synthesized by a simple soaking of anodized TNTs in the chloroplatinic (H2PtCl6) acid solution. Various techniques such as XRD, SEM, TEM, and XPS were used to characterize the materials and its catalytic property for the olefin reduction has been described along with a proposed mechanism. The Pt@TNT catalyst showed moderate to high catalytic conversions of styrene and its derivative to ethyl benzene-based products using hydrazine hydrate as a reducing agent.
Applied Materials Today, 2018, 10, 86–92. (IF- 8.01)
Web: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2352940717302913.