Two days First International Conference on “NanoMaterials and Sustainable Applications” (NANO-SA-2020) conducted at ICT-MARJ on Virtual Platform
05.12.2020
During this COVID -19, pandemic situation virtual conferences are booster dose of energy and knowledge. As a part of the virtual events, the First International Conference on “NanoMaterials and Sustainable Applications” (NANO-SA-2020) was organized by the Institute of Chemical Technology, Mumbai-Marathwada Campus, Jalna, India by virtual mode (Zoom webinar) on 2nd and 3rd December 2020. More than 900 participants from 20+ countries were registered for this conference including undergraduates, graduates, research scholars, faculty, and industrial researchers from various industries. NANO-SA-2020 conference was inaugurated by Prof. Aniruddha B. Pandit (Vice-Chancellor, ICT, Mumbai) and Prof. Smita Lele (Director, ICT-MARJ). These two days international conference was contributed twelve incredible talks on newly designed advanced nanomaterials and sustainable applications. This conference was commencing with an inaugural lecture of Padmashri Prof. G. D. Yadav. Also other eminent personalities around the world namely, Prof. Abhishek Dey, Prof. Vivek Polshettiwar, Dr. Jagadeesh Rajenahally, Prof. Paolo Fornasiero, Dr. Haresh Manyar, Prof. Tewodros Asefa, Prof. R. V. Jayaram, Dr. Rajendra Srivastava, Prof. Parasuraman Selvam, Dr. E. Balaraman, and Prof. B. M. Bhanage also share their views in the field of nanocatalysis for sustainability.
This conference provides a platform for researchers from across the world to communicate and share the latest developments and applications of nanomaterials in the developing and ever-expanding fields like energy conversion (Fuel cells & Hydrogen), nanocatalyzed organic transformations, carbon capture, storage, and conversion (CO2 sequestration), environmental remediation and sustainable applications (viz. organic methodologies) said by Prof. Gawande, Convener of the conference. This unique theme, nanomaterials for sustainable applications provides a new avenue for the researcher to design and development of nanomaterials for a sustainable future, added Prof. Gawande.
The NANO-SA-2020 ended with a valedictory ceremony which was graced by a distinguished ICT faculty, Prof. B. M. Bhanage, Professor and Dean (Infrastructure and Campus Development), ICT, Mumbai. Prof. Bhanage. enlighten valuable suggestions for researchers, Dr. Girish Joshi and Dr. Parag Nemade summarised the proceeding of two days conference. Finally, the vote of thanks given by Dr. Manoj Jadhao. This event throughout hosted by Dr. Ritika Joshi. Gawande’s group actively involved in the organizing and arrangement of the conference.
Web: http://www.ictsusnanomaterials.com/

Prof. Manoj B. Gawande featured in Stanford University's global list of top 2% scientists for the year 2019 in the Chemistry field, Heartly Congratulations….!!!
30.11.2020
Prof. Manoj B. Gawande featured in Stanford University’s global list of top 2% scientists for the year 2019 in the Chemistry field with RCPTM, Czech Republic institute affiliation.
Web: https://data.mendeley.com/datasets/btchxktzyw/2
(file: table-S7-singleyr-2019 in the link)



New CSIR-JRF, Mr. Gajanan who joined as PhD students of Prof. Gawandes research group at ICT-MARJ Campus on November 09, 2020
09.11.2020
Welcome to new group member Mr. Gajanan Y. Shinde, as a PhD student, who joined Prof. Gawandes research group at ICT-MARJ Campus. He qualified CSIR NET-JRF examination in August 2019 as well as SET and Gate exams conducted by respective authorities. Also, he has considerable research experience as a Project Assistant II position at CSIR NCL Pune (on a major research project entitled “Innovative processes and technologies for Indian pharmaceutical and agrochemical industries (INPROTICS)”.
We congratulate and welcome Gajanan in Prof. Gawandes research group at ICT-MARJ family……!!!
Our recently published paper selected as “Editorial Choice Paper”
29.10.2020
We (RCPTM/ICT team) recently published paper “Mechanochemical synthesis of Cu2S bonded 2D-sulfonated organic polymers: continuous production of dimethyl carbonate (DMC) via preheating of reactants” Green Chem., 2020, 22, 5619-5627; DOI: 10.1039/D0GC01030H.
This research paper selected as a “Editorial Choice Paper” and “Feature Cover” These selected papers are freely available till January 2021. Pls see the below details,

Prof. Gawande’s work highlighted in Chemistry views and selected as "Feature Cover"
10.10.2020
We (RCPTM/ICT team) recently published the paper entitled “Mesoporous P‐ and F‐co‐doped Amorphous Carbon Nitride: Nanocatalysts for Photocatalytic CO2 Reduction and Thermocatalytic Furanics Synthesis from Sugars” ChemSusChem, 2020, 13, 5231-5238 highlighted in Chemistry Views.
Chemistry Views is the online science news magazine of Chemistry Europe, an organization of 16 European chemical societies. It informs about what is happening in the global chemistry community and has a strong focus on the people behind the science.
For more details see the YouTube video published by Chemistry Views on https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Z0GyEE47lCA&feature=emb_logo
Prof. Gawande and colleagues have developed new P- and F-co-doped amorphous carbon nitride materials. The synthesized material has a mesoporous structure, shows good visible light absorption, and has a large surface area. The doping with P- and F-atoms narrows the optical band gap and enables an excellent photocatalytic activity for the aqueous reduction of carbon dioxide into methanol under visible-light irradiation. The activity is fifteen times higher than that of pure carbon nitride. The doping also turns the material into an acid-base bifunctional catalyst that is suitable for the thermal conversion of carbohydrates (glucose and xylose) into high-value furanic compounds (5-hydroxymethyl-2-furaldehyde (HMF) and furfural).
This article was also selected as a “Feature Cover” in the ChemSusChem journal.
Web: https://chemistry-europe.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/cssc.202001172


Singh and co-workers published a review entitled “Functional Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Catalysis and Environmental Applications” in the Bulletin of the Chemical Society of Japan and selected for a "Feature Cover"
22.07.2020
Bulletin of the Chemical Society of Japan, 2020, DOI: 10.1246/bcsj.20200136; (IF-4.48)
Web: https://www.journal.csj.jp/doi/full/10.1246/bcsj.20200136

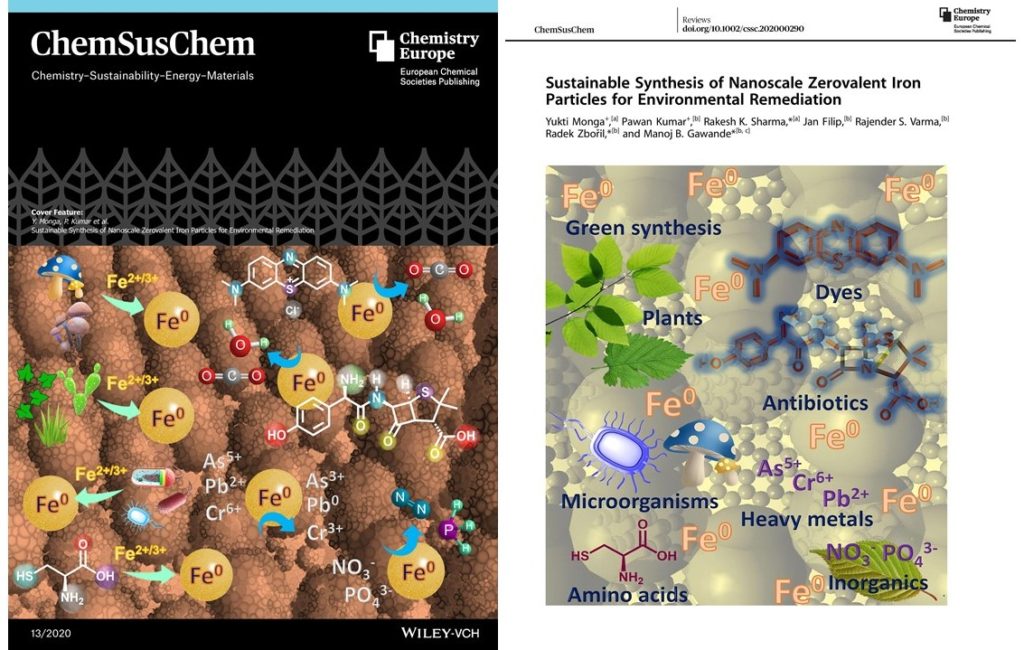
Monga et al. published a review entitled “Sustainable synthesis of nanoscale zerovalent iron particles for environmental remediation” in ChemSusChem and selected as a "Feature Cover" , 2020
29.06.2020
The transition metal iron(Fe) is the fourth most abundant element in the earth’s crust, can play a crucial role in diminishing the environment pollutants ie. Good catalytic properties for environmental remediation, also useful for various organic transformations, biomedical applications, and development of environmentally benign technologies due to its less toxic nature, biocompatibility, as well as high catalytic activity as compared to other noble and non-noble metals. In this review, Monga et al. summarized various green synthesis pathways for preparation of nanoscale zerovalent iron (nZVI) which are advantageous over other reported conventional chemical and physical methods. Also covered recently reported environmentally benign methods for the synthesis of nZVI along with their properties and interactions with diverse biomolecules are described in the consequence of environmental remediation and catalysis. This review helpful for researchers to design and develop novel environmentally sustainable processes for the synthesis of various catalytic materials which can be benefited in pollutant removal and degradation, disinfection, and catalysis.
ChemSusChem, 2020, DOI: 10.1002/cssc.202000290, (IF-7.96)
Web: https://chemistry-europe.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/cssc.202000290
Agnieszka et al. article entitled “Graphitic carbon nitride-nickel catalyst: from material characterization to efficient ethanol electrooxidation” published in ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering
08.04.2020
Today in catalysis, metal nanoparticles (NPs) used as a catalyst and its properties strongly depend on their size and dispersity on the catalyst support. Interactions between metal NPs and supporting medium influences the electronic structure of the catalyst as well as its stability and durability. Various carbon based material like carbon black, carbon nanotubes, graphene sheets or carbonaceous materials doped with boron, nitrogen or sulphur are employed as a supporting medium in catalyst development. In this article, we have reported synthesis of nickel doped graphitic carbon nitride (Ni/gCN(H) as a catalyst. This Ni-doped g-carbon nitride (Ni/gCN(H)) demonstrated for electrochemical activity in ethanol electrooxidation which is competitive with other Ni-based catalysts.
ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2020, DOI: 10.1021/acssuschemeng.0c02267, (IF-6.97)
Web: https://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/acssuschemeng.0c02267

Our review article entitled “Recent development of covalent organic frameworks (COFs): synthesis and catalytic (organic-electro-photo) applications” published in Materials Horizons
19.02.2020
We (RCPTM/ICT team) have published this important review jointly with Prof. Markus Antoinette (Max Planck Institute, Germany) and Prof. R. K. Sharma (DU, India). This review summarizes selected and most recent synthetic methodologies for their assembly including the formation of magnetic COFs. Potential insights in the field of catalysis; electrocatalysis; and photocatalysis, where COFs can serve as excellent platforms for supporting catalytic species, are also illustrated.
Mater. Horiz. 2020, 7,411-454 DOI: 10.1039/C9MH00856J
Web: https://pubs.rsc.org/ko/content/articlelanding/2020/mh/c9mh00856j/unauth#!divAbstract

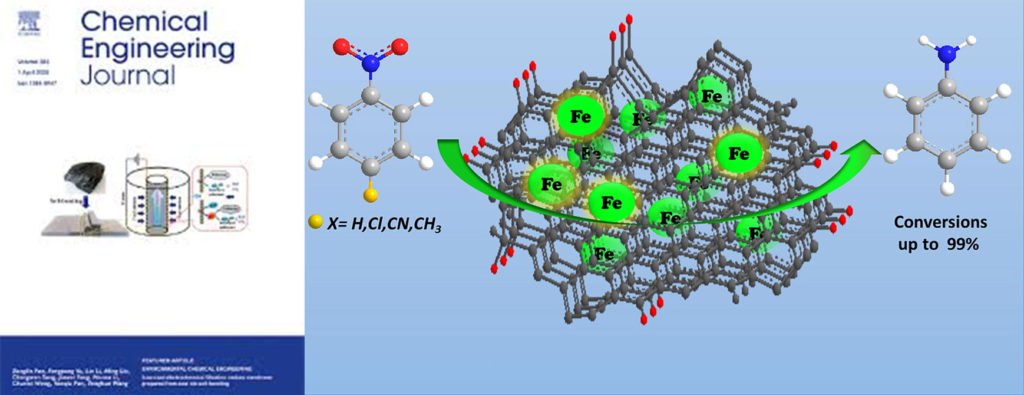
The research article entitled “Fe (0)-embedded thermally reduced graphene oxide as efficient nanocatalyst for reduction of nitro compounds to amines” by Goswami-Kadam et al. published in Chemical Engineering Journal
15.02.2020
Reduced graphene oxide (rGO) has emerged as a unique supporting material due to its high specific surface area, and high electron mobility on its surface facilitating the better charge transportation which utilized for diverse applications in photocatalysis, spintronics, energy storage, as well as catalytic organic transformations. In this article Goswami-Kadam et al. reported a highly active Fe(0)-embedded reduced graphene oxide (Fe/TRGO) catalyst for the selective reduction of nitro compounds. They prepared catalyst through hydrogen-assisted pyrolytic step by using GO and Fe salt as precursors.
Chemical Engineering Journal 2020, 382, 122469.
Web: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1385894719318728
Our work on “Sulfonated dendritic mesoporous silica nanospheres: a metal-free Lewis acid catalyst for the upgrading of carbohydrates” is published in the reputed journal Green Chemistry
03.02.2020
In this collaboration work with Prof. Marcio, we have reported upgrading of several mono-, di- and polysaccharides such as xylose, fructose, glucose, sucrose, and cellulose to valuable platform chemicals using a novel catalyst comprising sulfonated dendritic mesoporous silica nanospheres. Additionally, a thorough comparative study was conducted encompassing arrays of sulfonated silicas as catalysts with the aim of relating their activities and appreciating the features which could be responsible for their activity.
Green Chemistry, 2020, 22, 1754-1762 DOI: 10.1039/C9GC03489G
Web: https://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlelanding/2020/gc/c9gc03489g#!divAbstract
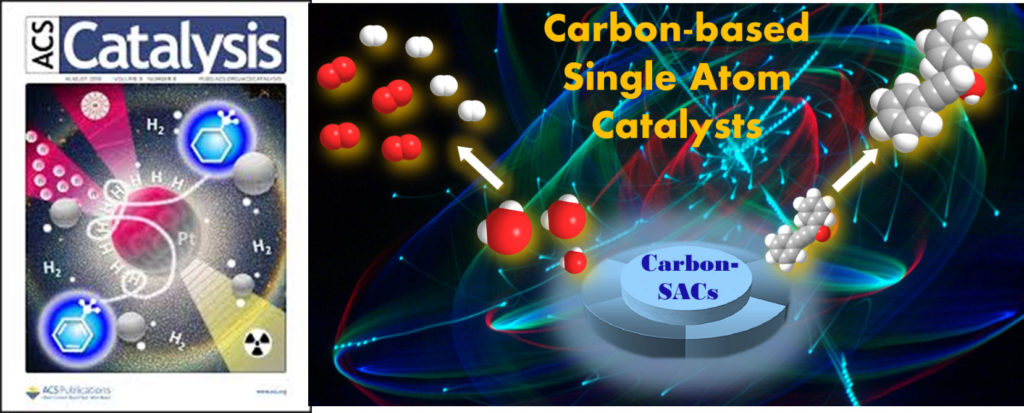
Prof. Gawande published an invited review article entitled “Carbon-based Single-Atom Catalysts for Advanced Applications” in ACS Catalysis
10.01.2020
In this review article, we report the progress of carbon-based single-atom catalysts, including primary metals such as Co, Cu, Zn, Pd, Ni, Pt, among others, embedded in carbon matrices and applied to applications in organic catalysis, photocatalysis, and electrocatalysis. It is important to point out that the main focus of this review is directed to the activity and applications of single-atom catalysts, which are discussed in detail; thus, characterization and rationalization are excluded. Finally, we provide a future perspective on the development and progress made on a carbon-based single metal atom for catalysis.
ACS Catalysis 2020, 10, 2231-2259 (IF-12.22)