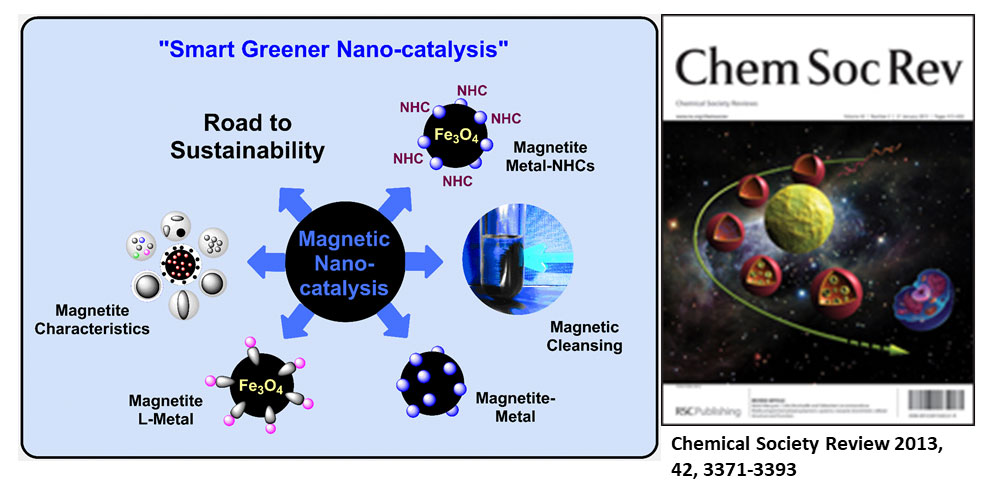
Gawande et al. review article entitled “Nano-magnetite (Fe3O4) as a support for recyclable catalysts in the development of sustainable methodologies” published in Chemical Society Review, “Highly Cited Article” 2013.
18.02.2013
Magnetite is a well-known material, also known as ferrite (Fe3O4). In this review article, synthesis and surface modification of nano-magnetite materials with homogeneous metals, organoligands, organocatalysts, N-heterocyclic carbenes (NHC), as well as chiral catalysts and their applications in catalysis and synthetic organic chemistry briefly summarised. The main theme of this article is to use nano-magnetite (Fe3O4) as a support for the immobilization of catalysts which shows versatile catalytic activity during various organic transformations.
Chemical Society Review, 2013, 42, 3371-3393. (IF- 40.44) “Highly cited article” more than > 1000 citations
Web: https://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlelanding/2013/cs/c3cs35480f/unauth#!divAbstract
Dr. Gawande joined as Senior Researcher and Head (Nanocatalysis Laboratory) at Palacky University, Czech Republic.
Heartly Congratulations…...!!!
11th July 2013
Dr. Manoj B. Gawande joined as Head and Senior Researcher at Nanocatalysis Laboratory, Regional Centre of Advanced Technologies and Materials, Faculty of Science, Department of Physical Chemistry, Palacky University, Šlechtitelů 27, 783 71, Olomouc, Czech Republic. His research group focused on several research activities including the development of well-defined morphology dependent catalysts, single-atom catalysts, core-shell, and yolk-shell nanocatalysts, silica-based hybrid catalysts, 2 D graphene-based materials and 2D single metal or mixed metal ionic nanocatalysts. Nanoparticles are regarded as attractive candidates for heterogeneous catalysis in various imperative catalytic processes as they are easy to synthesize with a desired size, structure, morphology and composition. Keeping in mind the current environmental sustainability concerns, it is important to design inexpensive and benign nanocatalysts for organic transformations/catalytic processes. These hot research areas aim to design the materials based on highly important targeted catalytic, organic transformations and Photo (electro) catalysis applications.

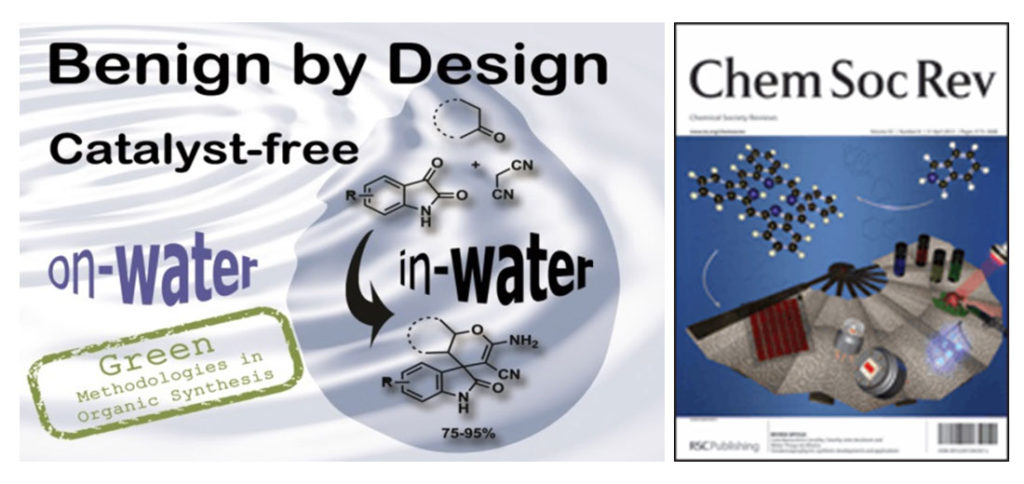
Gawande et al. review article “Benign by Design: Catalyst-Free in-water, on-water Green Chemical Methodologies in Organic Synthesis” published in Chemical Society review, 2013.
2013
In this review article various named reactions, multicomponent reactions, and the synthesis of heterocyclic compounds are summarized by using various energy input systems such as microwave and ultrasound irradiation with many other methods. The main aim of this review article is to provide outline about the catalyst-free reactions in aqueous media which helps to design benign methodologies for organic synthesis by academia and industrial practitioners using alternative energy inputs based on fundamental techniques.
Chemical Society Review, 2013, 42, 5522-5551. (IF- 40.44)
Web: https://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlelanding/2013/cs/c3cs60025d/unauth#!divAbstract
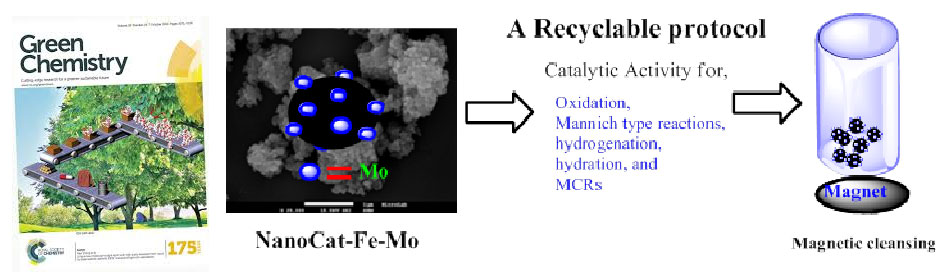
Gawande et al. article entitled “Catalytic applications of a versatile magnetically separable Fe-Mo nanocatalyst” published in Green Chemistry and selected as “Hot article of the week” by editorial choice, 2013.
2013
Nanoparticles attract attention due to its special properties as compared to bulk metal counterparts, having multidisciplinary applications in areas including drug discovery, energy storage, electronic devices, and heterogeneous catalysis. In nanocatalyst, magnetic nanocatalysts emerged as highly promising and versatile nanoentities combining high surface areas and excellent catalytic activities. Gawande et al. reported synthesis of novel, highly active and versatile Nanocat-Fe-Mo catalyst by simple wet impregnation/precipitation method. This Fe-Mo nanomaterial is catalytically active and highly selective for a wide range of organic conversions including oxidations, A3 couplings, hydrogenations, and hydrations.
Green Chemistry, 2013, 15, 682-689.
Web- Hot article of week by editorial choice: http://blogs.rsc.org/gc/2013/02/08/hot-articles-of-the-week/
Web: https://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlelanding/2013/gc/c3gc36844k#!divAbstract